Millions of people worldwide suffer from vision problems, but not all eye conditions are the same. Two of the most common causes of vision loss are macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy. While both can damage eyesight, they have different causes, risk factors, and treatment options.
If you or a loved one is struggling with vision changes, understanding these conditions can help you make informed decisions about eye care. Let’s break down the key differences between macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy and how they affect vision.
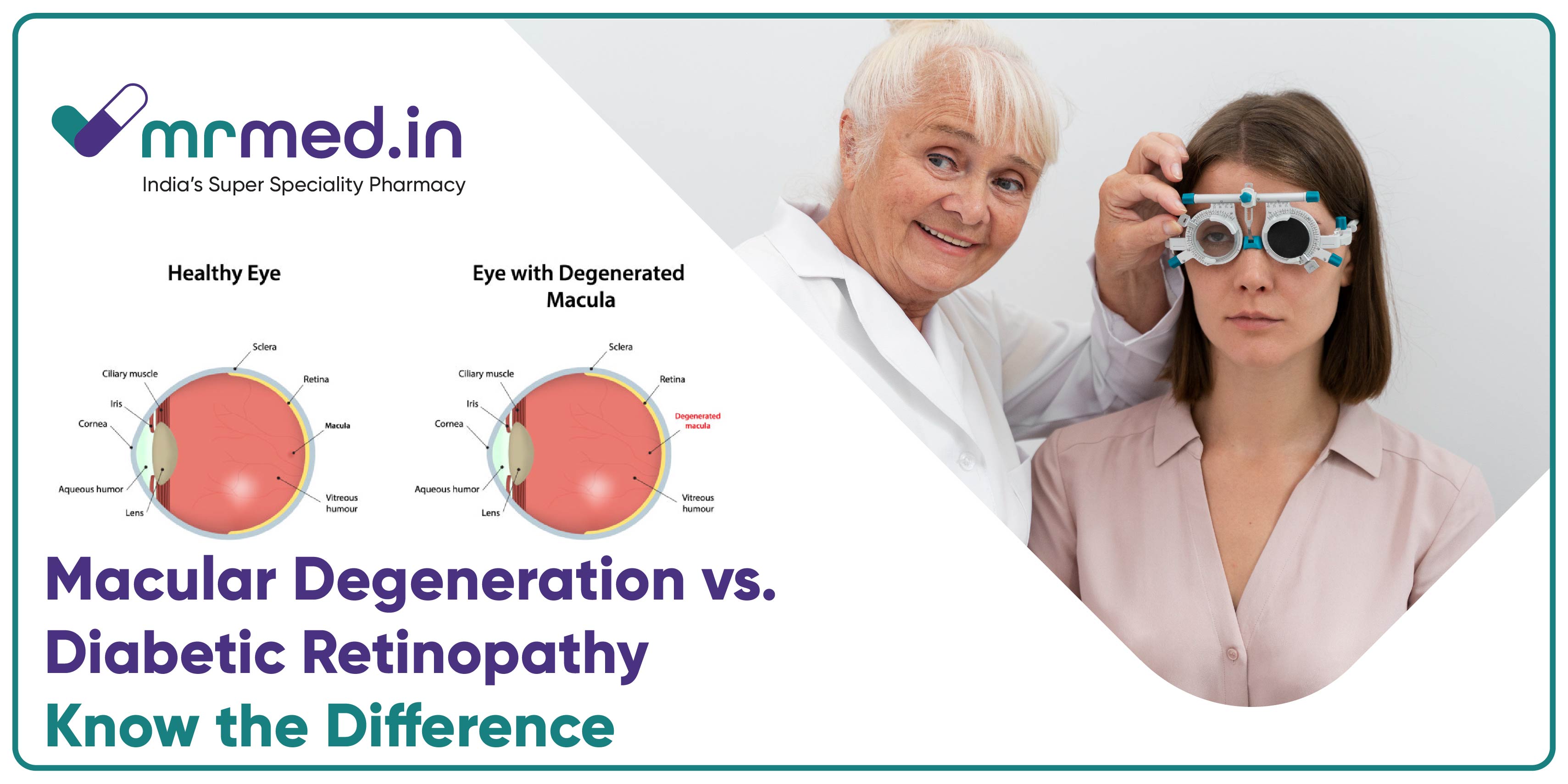
What Is Macular Degeneration?
It is also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD), is an eye condition that affects the macula—the part of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision. It primarily occurs in older adults and can lead to blurred or distorted vision over time.
There are two types of macular degeneration:
Dry AMD – The most common type, where the macula gradually thins, leading to vision loss over the years.
Wet AMD – A more severe form where abnormal blood vessels grow under the retina, causing sudden and serious vision loss.
People with AMD may struggle with reading, recognising faces, or seeing fine details, but peripheral vision usually remains intact.
What Is Diabetic Retinopathy?
It is an eye disorder linked to diabetes, where elevated blood sugar levels harm the small blood vessels in the retina. This damage can result in leakage, swelling, and scarring, eventually leading to blurred vision, dark spots, and, if untreated, potential blindness.
There are two main stages:
Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR) – Early-stage retinopathy where small blood vessels leak, causing mild vision problems.
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR) – Advanced retinopathy where new, fragile blood vessels grow and bleed into the retina, leading to severe vision loss.
Uncontrolled diabetes and hypertension (high blood pressure) increase the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
What Are the Symptoms of Each Condition?
Feature | Macular Degeneration | Diabetic Retinopathy |
Main cause | Ageing, genetic factors | High blood sugar from diabetes |
Main symptom | Blurry or distorted central vision | Blurry vision, dark spots, floaters |
Vision loss type | Central vision affected | Both central and peripheral vision are affected |
Progression | Gradual (Dry AMD), sudden (Wet AMD) | Slows at first, worsens if untreated |
How Are These Eye Diseases Treated?
Macular Degeneration Treatment
While there is no cure for AMD, treatments can help slow its progression. Some options include:
Lifestyle Changes – A diet rich in leafy greens, omega-3s, and antioxidants can support eye health.
Anti-VEGF Injections – Medications like Eylea Injection help slow abnormal blood vessel growth in wet AMD.
Low Vision Aids – Magnifiers and special glasses can help people with vision loss manage daily tasks.
Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment
Managing diabetes is the key to controlling diabetic retinopathy. Treatments include:
Blood Sugar Control – Keeping blood sugar levels stable prevents further damage.
Laser Therapy – Used to seal leaking blood vessels and stop further damage.
Anti-VEGF Therapy – Helps reduce swelling and prevents new abnormal blood vessel growth.
Surgery – In severe cases, a procedure called vitrectomy removes blood from the eye.
How Do These Conditions Affect Daily Life?
Both macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy can make everyday tasks challenging. People may struggle with:
Reading, driving, or recognising faces.
Adjusting to dim lighting or bright glare.
Performing fine tasks like sewing or writing.
Some patients use presvu effectiveness for eye issues to support their vision, but early diagnosis and medical treatment remain the best ways to preserve eyesight.
Is There a Connection Between These Eye Conditions and Glaucoma?
Both macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy elevate the risk of glaucoma, a condition that damages the optic nerve. Pilocarpine, a medicine used to reduce eye pressure, can help manage glaucoma, but early detection is crucial.
In addition, Latanoprost is commonly prescribed to lower eye pressure in glaucoma patients, reducing the risk of further damage. Since diabetic retinopathy and glaucoma can occur together, it’s important for individuals with diabetes to get regular eye checkups.
Diabetes and hypertension are also major risk factors for glaucoma, making regular eye exams essential for those at risk.
Uncontrolled diabetes doesn’t just cause diabetic retinopathy—it can also cause serious eye conditions, including:
Blurry Vision – High blood sugar can temporarily affect the lens, causing vision fluctuations.
Cataracts – Diabetics are more likely to develop cataracts at a younger age.
Glaucoma – Increased eye pressure can lead to permanent vision loss.
Retinal Detachment – Severe diabetic retinopathy can cause scar tissue that pulls the retina away from the eye.
These side effects of diabetes highlight the significance of routine eye checkups and maintaining stable blood sugar levels to prevent vision complications.
Can Lifestyle Changes Help Prevent Vision Loss?
Yes! While some risk factors like ageing or genetics can’t be changed, lifestyle choices play a huge role in protecting eyesight. Here’s what can help:
Eat a healthy diet – Leafy greens, fish, and nuts support eye health.
Control blood sugar and blood pressure – This is especially important for diabetics.
Quit smoking – Smoking elevates the risk of AMD and other vision problems.
Wear sunglasses – UV protection can help prevent eye damage.
Get regular eye checkups – Early detection leads to better treatment outcomes.
Final Thoughts
Both macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy are serious eye conditions that can lead to blindness/vision loss if ignored. However, early detection, medical treatment, and lifestyle changes can help slow progression and protect eyesight.
If you notice any changes in vision, don’t wait—schedule an eye exam. Prioritising your eye health now can help you avoid major vision issues later.




 SURVEY
How Did You Hear About Us?
SURVEY
How Did You Hear About Us?





























Comments